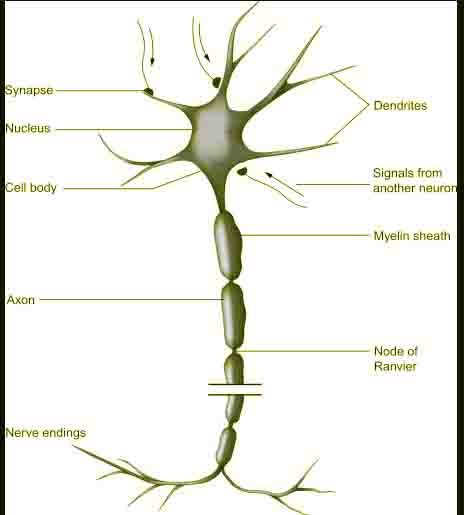
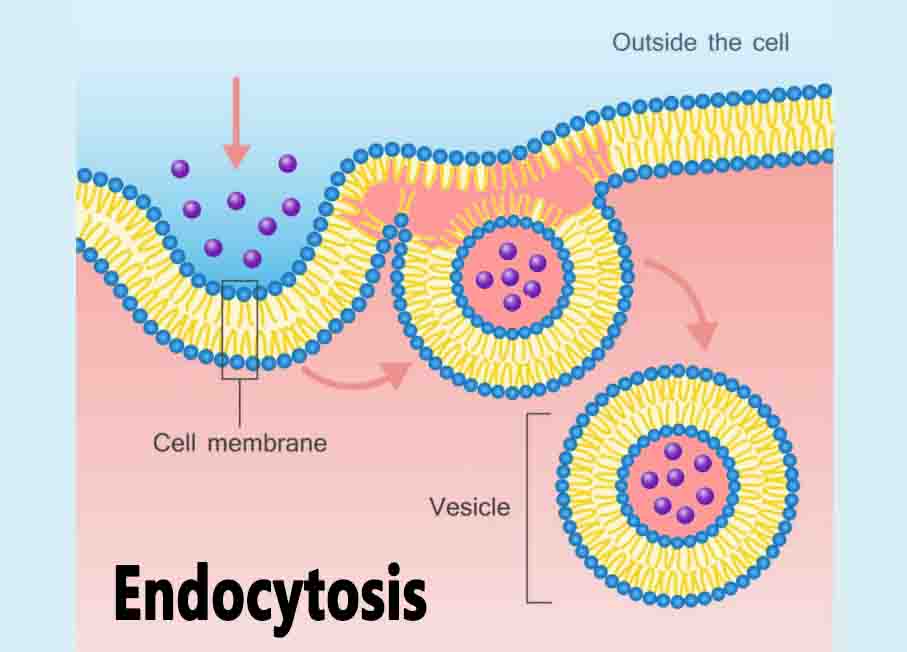
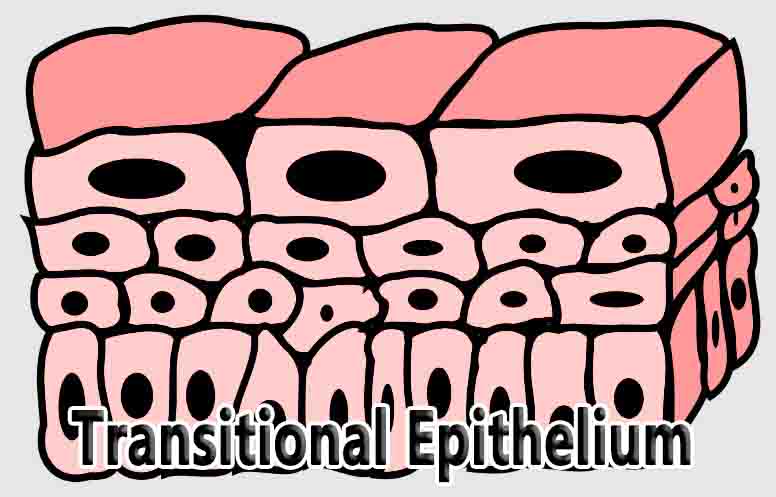
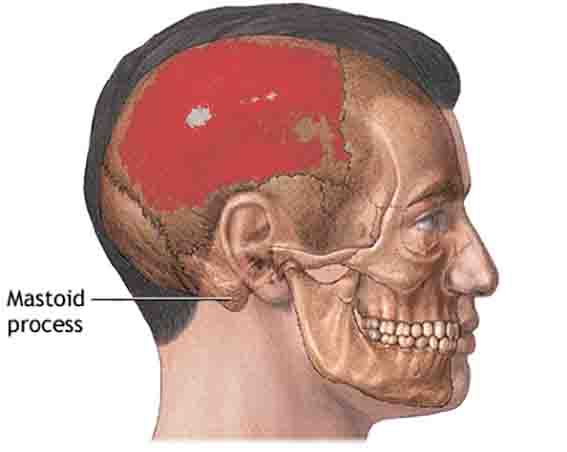
Sensory Neuron
Definition A sensory neuron (sometimes referred to as an afferent neuron) is a nerve cell that detects and responds to external signals. Sensory neurons receive information via their receptors, which are part of the peripheral nervous system, and convert this information into electrical impulses. These impulses act as signals and are passed on to the … Read more